PINE LIBRARY
Cập nhật X
Library "X"
a collection of 'special' methods/functions ('special' at the time of conception)
Initial functions includes:
• count of a given number in a given array
• array.get() but option added to use negative index
• sum of all digits until the output < 10
• slope/angle calculation of lines
method count_num_in_array(arr, num)
counts how many times a given number is present in a given array (0 when not present)
Namespace types: int[]
Parameters:
arr (int[]): Array (int, float[])
num (int): Number that needs to be counted (int, float)
Returns: count of number in array (0 when not present)
method count_num_in_array(arr, num)
Namespace types: float[]
Parameters:
arr (float[])
num (float)
method get_(arr, idx)
array.get() but you can use negative index (-1 is last of array, -2 is second last,...)
Namespace types: int[]
Parameters:
arr (int[]): Array (int, float, string, bool, label, line, box, color[])
idx (int): Index
Returns: value/object at index, 'na' if index is outside array
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: float[]
Parameters:
arr (float[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: string[]
Parameters:
arr (string[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: bool[]
Parameters:
arr (bool[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: label[]
Parameters:
arr (label[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: line[]
Parameters:
arr (line[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: box[]
Parameters:
arr (box[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: color[]
Parameters:
arr (color[])
idx (int)
method sumAllNumbers_till_under_10(num)
sums all separate digit numbers, it repeats the process until sum < 10
Namespace types: series int, simple int, input int, const int
Parameters:
num (int): Number (int, float)
Returns: value between 0 and 9
method sumAllNumbers_till_under_10(num)
Namespace types: series float, simple float, input float, const float
Parameters:
num (float)
method XYaxis(width)
Global function to calculate Yaxis, which is used in calculate_slope() method
Namespace types: series int, simple int, input int, const int
Parameters:
width (int): Amount of bars for reference X-axis
Returns: Yaxis
method calculate_slope(width, XYratio, Yaxis, x1, y1, x2, y2)
Returns a normalised slope
Namespace types: series int, simple int, input int, const int
Parameters:
width (int): Amount of bars to calculate height
XYratio (float): Ratio to calculate height (from width) normalised_slope calculation
Yaxis (float): Y-axis from XYaxis() method
x1 (int): x1 of line
y1 (float): y1 of line
x2 (int): x2 of line
y2 (float): y2 of line
Returns: Tuple of [slope, angle] -> slope = price difference per bar
a collection of 'special' methods/functions ('special' at the time of conception)
Initial functions includes:
• count of a given number in a given array
• array.get() but option added to use negative index
• sum of all digits until the output < 10
• slope/angle calculation of lines
method count_num_in_array(arr, num)
counts how many times a given number is present in a given array (0 when not present)
Namespace types: int[]
Parameters:
arr (int[]): Array (int, float[])
num (int): Number that needs to be counted (int, float)
Returns: count of number in array (0 when not present)
method count_num_in_array(arr, num)
Namespace types: float[]
Parameters:
arr (float[])
num (float)
method get_(arr, idx)
array.get() but you can use negative index (-1 is last of array, -2 is second last,...)
Namespace types: int[]
Parameters:
arr (int[]): Array (int, float, string, bool, label, line, box, color[])
idx (int): Index
Returns: value/object at index, 'na' if index is outside array
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: float[]
Parameters:
arr (float[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: string[]
Parameters:
arr (string[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: bool[]
Parameters:
arr (bool[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: label[]
Parameters:
arr (label[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: line[]
Parameters:
arr (line[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: box[]
Parameters:
arr (box[])
idx (int)
method get_(arr, idx)
Namespace types: color[]
Parameters:
arr (color[])
idx (int)
method sumAllNumbers_till_under_10(num)
sums all separate digit numbers, it repeats the process until sum < 10
Namespace types: series int, simple int, input int, const int
Parameters:
num (int): Number (int, float)
Returns: value between 0 and 9
method sumAllNumbers_till_under_10(num)
Namespace types: series float, simple float, input float, const float
Parameters:
num (float)
method XYaxis(width)
Global function to calculate Yaxis, which is used in calculate_slope() method
Namespace types: series int, simple int, input int, const int
Parameters:
width (int): Amount of bars for reference X-axis
Returns: Yaxis
method calculate_slope(width, XYratio, Yaxis, x1, y1, x2, y2)
Returns a normalised slope
Namespace types: series int, simple int, input int, const int
Parameters:
width (int): Amount of bars to calculate height
XYratio (float): Ratio to calculate height (from width) normalised_slope calculation
Yaxis (float): Y-axis from XYaxis() method
x1 (int): x1 of line
y1 (float): y1 of line
x2 (int): x2 of line
y2 (float): y2 of line
Returns: Tuple of [slope, angle] -> slope = price difference per bar
Phát hành các Ghi chú
v2Update -> examples
Phát hành các Ghi chú
v3DETAILS:
count_num_in_array()
Typically, we use loops for counting how many values an array contains. With count_num_in_array(), we don't use a loop, but the build-in functions array.sort(), array.includes(), array.lastindexof() and array.indexof()
This should give us better performance due to using less loops
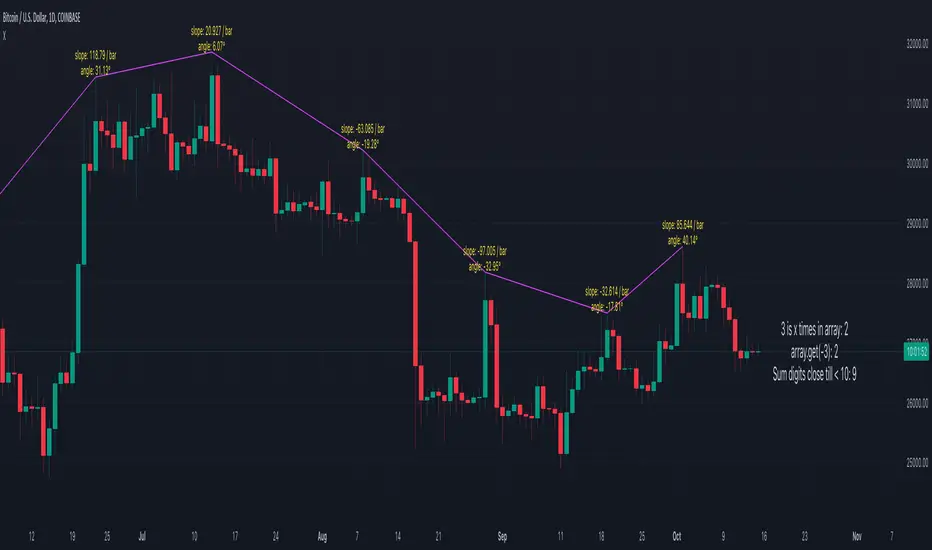
-> Seen on chart at right label: 4 is x times in array -> 2, from array (3, 4, 3, 0, 1 , 2, 3, 4)
get_()
array.get() can only be used with a positive index, indexes as -1, -2, ... are not allowed.
For the ones who want to, the get_() function is able to use negative indexes
-> Seen on chart at right label: array.get(-3) -> 2, from array (3, 4, 3, 0, 1 , 2, 3, 4)
sumAllNumbers_till_under_10()
There are people who believe in the power of certain numbers between 0 and 9, they count every digit until they end up with a number between 0 and 9
For example -> count every digit of 123456 -> 1+2+3+4+5+6 = 21, if the sum is higher then 9, repeat -> 2+1 = 3
It was not so easy to create a function which uses as less string manipulation as possible (more string manupulation is greater risk for memory errors)
I finally ended up with sumAllNumbers_till_under_10()
-> Seen on chart at right label: Sum digits of close price until number < 10.
XYaxis(), calculate_slope()
Angle / slope calculation is tricky due to different units in X and Y axis (bar_index vs. price)
Also, certain techniques give very different result when comparing historical data, due to price fluctuations.
With the techniques in XYaxis() and calculate_slope() I tried to create angles / slopes which are rather similar on all bars.
Importantly, XYaxis() always needs to be placed globally, calculate_slope() can be placed locally.
The XYratio can be useful for finetuning, since every user has other habits regarding zooming in on the chart. Zooming in/out doesn't
change bars/price, but it does change our angle perspective. Therefore XYratio can be very useful (for example as input.float(3, '', minval=0, maxval=10))
-> Seen on chart as purple lines + labels with slope/angle
Phát hành các Ghi chú
v4Added namespace & description for each overload
Updated:
method count_num_in_array(arr, num)
counts how many times a given number is present in a given array (0 when not present)
Namespace types: float[]
Parameters:
arr (float[]): array<float>
num (float): Number that needs to be counted (int, float)
Returns: count of number in array (0 when not present)
method get_(arr, idx)
array.get() but you can use negative index (-1 is last of array, -2 is second last,...)
Namespace types: color[]
Parameters:
arr (color[]): array<color>
idx (int): Index
Returns: value/object at index, 'na' if index is outside array
method sumAllNumbers_till_under_10(num)
sums all separate digit numbers, it repeats the process until sum < 10
Namespace types: series float, simple float, input float, const float
Parameters:
num (float): Number (float)
Returns: value between 0 and 9
Phát hành các Ghi chú
v5Added:
method testMa(iType, src, len)
Returns a ma with simple int length (for comparison against xma() which can use series int length )
Namespace types: series string, simple string, input string, const string
Parameters:
iType (string): Type of ma (ema, dema, tema, rma, hullMa or linreg)
src (float): Source
len (simple int): Length
Returns: Moving Average
method wma_arr(source, len)
Returns a wma, used in HullMa (in xma() )
Namespace types: float[]
Parameters:
source (float[]): array of source
len (int): Length
Returns: WMA
method xma(xma, type, src, len)
Returns a ma with series int length (for comparison against testMa() which can use simple int length )
Namespace types: xma
Parameters:
xma (xma): UDT object -> xma.new()
type (string)
src (float): Source
len (int): Length
Returns: Moving Average
xma
Fields:
ma1 (series__float)
ma2 (series__float)
ma3 (series__float)
ma4 (series__float)
xma (series__float)
aSrc (array__float)
aXma (array__float)
Phát hành các Ghi chú
v6 + example testMa and array MA (xma)Phát hành các Ghi chú
v7Added:
isDark()
Returns a boolean output, true when the chart background is dark, false if otherwise
method round_sig(number, round_to, only_R)
Returns a rounded number after isolating x significant numbers
Namespace types: series float, simple float, input float, const float
Parameters:
number (float): number to round
round_to (int): round to x sign. figures
only_R (bool): if enabled, when number > 1 only the values at the right of decimal point are considered
Returns: Rounded number to x significant figures
Phát hành các Ghi chú
v8Small bugfix in "examples"
Phát hành các Ghi chú
v10Added:
lastSundayOfMonth()
Just import the library, for example:
import fikira/X/10
plot(X.lastSundayOfMonth('THU'))
The optional 'adj' can be used on certain pairs (forex for example) where the start of the week is Sunday, and not Monday
For example, on the EURUSD pair you can add 1 as 'adj':
import fikira/X/10
plot(X.lastSundayOfMonth('THU', 1))
lastSundayOfMonth(DAY, adj)
lastSundayOfMonth(): Shows last x day of the month
Parameters:
DAY (string)
adj (int): (optional): add/subtract 1 when needed (for example on FOREX pairs)
Returns: int (day of month)
Phát hành các Ghi chú
v11Added:
emas(source, start, stop)
Returns an array of ema's of different lengths (between `start` and `stop`)
Parameters:
source (float): Source (default close)
start (int): First (lowest) length value (default 10)
stop (int): Last (highest) length value (default 100)
Returns: Array of EMAs (default 90 ema values between length 10-100)
Thư viện Pine
Theo đúng tinh thần TradingView, tác giả đã công bố mã Pine này như một thư viện mã nguồn mở để các lập trình viên Pine khác trong cộng đồng có thể tái sử dụng. Chúc mừng tác giả! Bạn có thể sử dụng thư viện này cho mục đích cá nhân hoặc trong các ấn phẩm mã nguồn mở khác, nhưng việc tái sử dụng mã này trong các ấn phẩm phải tuân theo Nội Quy.
Who are PineCoders?
tradingview.com/chart/SSP/yW5eOqtm-Who-are-PineCoders/
TG Pine Script® Q&A: t.me/PineCodersQA
- We cannot control our emotions,
but we can control our keyboard -
tradingview.com/chart/SSP/yW5eOqtm-Who-are-PineCoders/
TG Pine Script® Q&A: t.me/PineCodersQA
- We cannot control our emotions,
but we can control our keyboard -
Thông báo miễn trừ trách nhiệm
Thông tin và các ấn phẩm này không nhằm mục đích, và không cấu thành, lời khuyên hoặc khuyến nghị về tài chính, đầu tư, giao dịch hay các loại khác do TradingView cung cấp hoặc xác nhận. Đọc thêm tại Điều khoản Sử dụng.
Thư viện Pine
Theo đúng tinh thần TradingView, tác giả đã công bố mã Pine này như một thư viện mã nguồn mở để các lập trình viên Pine khác trong cộng đồng có thể tái sử dụng. Chúc mừng tác giả! Bạn có thể sử dụng thư viện này cho mục đích cá nhân hoặc trong các ấn phẩm mã nguồn mở khác, nhưng việc tái sử dụng mã này trong các ấn phẩm phải tuân theo Nội Quy.
Who are PineCoders?
tradingview.com/chart/SSP/yW5eOqtm-Who-are-PineCoders/
TG Pine Script® Q&A: t.me/PineCodersQA
- We cannot control our emotions,
but we can control our keyboard -
tradingview.com/chart/SSP/yW5eOqtm-Who-are-PineCoders/
TG Pine Script® Q&A: t.me/PineCodersQA
- We cannot control our emotions,
but we can control our keyboard -
Thông báo miễn trừ trách nhiệm
Thông tin và các ấn phẩm này không nhằm mục đích, và không cấu thành, lời khuyên hoặc khuyến nghị về tài chính, đầu tư, giao dịch hay các loại khác do TradingView cung cấp hoặc xác nhận. Đọc thêm tại Điều khoản Sử dụng.