OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Cập nhật Multi-Oscillator Adaptive Kernel | AlphaAlgos
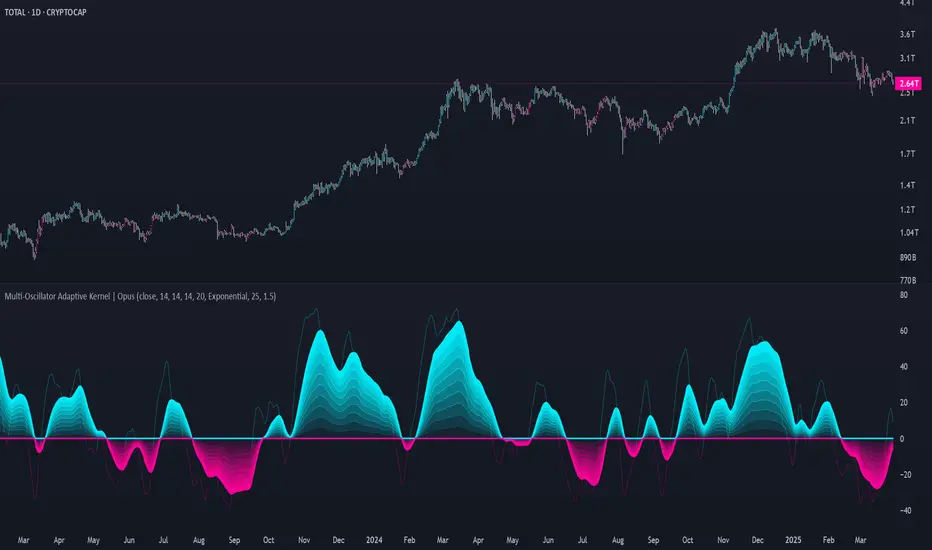
Multi-Oscillator Adaptive Kernel | AlphaAlgos
Overview
The Multi-Oscillator Adaptive Kernel (MOAK) is an advanced technical analysis tool that combines multiple oscillators through sophisticated kernel-based smoothing algorithms. This indicator is designed to provide clearer trend signals while filtering out market noise, offering traders a comprehensive view of market momentum across multiple timeframes.
Key Features
• Fusion of multiple technical oscillators (RSI, Stochastic, MFI, CCI)
• Advanced kernel smoothing technology with three distinct mathematical models
• Customizable sensitivity and lookback periods
• Clear visual signals for trend shifts and reversals
• Overbought/oversold zones for precise entry and exit timing
• Adaptive signal that responds to varying market conditions
Technical Components
The MOAK indicator utilizes a multi-layer approach to signal generation:
1. Oscillator Fusion
The core of the indicator combines normalized readings from up to four popular oscillators:
• RSI (Relative Strength Index) - Measures the speed and change of price movements
• Stochastic - Compares the closing price to the price range over a specific period
• MFI (Money Flow Index) - Volume-weighted RSI that includes trading volume
• CCI (Commodity Channel Index) - Measures current price level relative to an average price
2. Kernel Smoothing
The combined oscillator data is processed through one of three kernel functions:
• Exponential Kernel - Provides stronger weighting to recent data with exponential decay
• Linear Kernel - Applies a linear weighting from most recent to oldest data points
• Gaussian Kernel - Uses a bell curve distribution that helps filter out extreme values
3. Dual Signal Lines
• Fast Signal Line - Responds quickly to price changes
• Slow Signal Line - Provides confirmation and shows the underlying trend direction
Configuration Options
Oscillator Selection:
• Enable/disable each oscillator (RSI, Stochastic, MFI, CCI)
• Customize individual lookback periods for each oscillator
Kernel Settings:
• Kernel Type - Choose between Exponential, Linear, or Gaussian mathematical models
• Kernel Length - Adjust the smoothing period (higher values = smoother line)
• Sensitivity - Fine-tune the indicator's responsiveness (higher values = more responsive)
Display Options:
• Color Bars - Toggle price bar coloring based on indicator direction
How to Interpret the Indicator
Signal Line Direction:
• Upward movement (teal) indicates bullish momentum
• Downward movement (magenta) indicates bearish momentum
Trend Shifts:
• Small circles mark the beginning of new uptrends
• X-marks indicate the start of new downtrends
Overbought/Oversold Conditions:
• Values above +50 suggest overbought conditions (potential reversal or pullback)
• Values below -50 suggest oversold conditions (potential reversal or bounce)
Trading Strategies
Trend Following:
• Enter long positions when the signal line turns teal and shows an uptrend
• Enter short positions when the signal line turns magenta and shows a downtrend
• Use the slow signal line (area fill) as confirmation of the underlying trend
Counter-Trend Trading:
• Look for divergences between price and the indicator
• Consider profit-taking when the indicator reaches overbought/oversold areas
• Wait for trend shift signals before entering counter-trend positions
Multiple Timeframe Analysis:
• Use the indicator across different timeframes for confirmation
• Higher timeframe signals carry more weight than lower timeframe signals
Best Practices
• Experiment with different kernel types for various market conditions
• Gaussian kernels often work well in ranging markets
• Exponential kernels can provide earlier signals in trending markets
• Combine with volume analysis for higher probability trades
• Use appropriate stop-loss levels as the indicator does not guarantee price movements
This indicator is provided as-is with no guarantees of profit. Always use proper risk management when trading with any technical indicator. Nothing is financial advise.
Overview
The Multi-Oscillator Adaptive Kernel (MOAK) is an advanced technical analysis tool that combines multiple oscillators through sophisticated kernel-based smoothing algorithms. This indicator is designed to provide clearer trend signals while filtering out market noise, offering traders a comprehensive view of market momentum across multiple timeframes.
Key Features
• Fusion of multiple technical oscillators (RSI, Stochastic, MFI, CCI)
• Advanced kernel smoothing technology with three distinct mathematical models
• Customizable sensitivity and lookback periods
• Clear visual signals for trend shifts and reversals
• Overbought/oversold zones for precise entry and exit timing
• Adaptive signal that responds to varying market conditions
Technical Components
The MOAK indicator utilizes a multi-layer approach to signal generation:
1. Oscillator Fusion
The core of the indicator combines normalized readings from up to four popular oscillators:
• RSI (Relative Strength Index) - Measures the speed and change of price movements
• Stochastic - Compares the closing price to the price range over a specific period
• MFI (Money Flow Index) - Volume-weighted RSI that includes trading volume
• CCI (Commodity Channel Index) - Measures current price level relative to an average price
2. Kernel Smoothing
The combined oscillator data is processed through one of three kernel functions:
• Exponential Kernel - Provides stronger weighting to recent data with exponential decay
• Linear Kernel - Applies a linear weighting from most recent to oldest data points
• Gaussian Kernel - Uses a bell curve distribution that helps filter out extreme values
3. Dual Signal Lines
• Fast Signal Line - Responds quickly to price changes
• Slow Signal Line - Provides confirmation and shows the underlying trend direction
Configuration Options
Oscillator Selection:
• Enable/disable each oscillator (RSI, Stochastic, MFI, CCI)
• Customize individual lookback periods for each oscillator
Kernel Settings:
• Kernel Type - Choose between Exponential, Linear, or Gaussian mathematical models
• Kernel Length - Adjust the smoothing period (higher values = smoother line)
• Sensitivity - Fine-tune the indicator's responsiveness (higher values = more responsive)
Display Options:
• Color Bars - Toggle price bar coloring based on indicator direction
How to Interpret the Indicator
Signal Line Direction:
• Upward movement (teal) indicates bullish momentum
• Downward movement (magenta) indicates bearish momentum
Trend Shifts:
• Small circles mark the beginning of new uptrends
• X-marks indicate the start of new downtrends
Overbought/Oversold Conditions:
• Values above +50 suggest overbought conditions (potential reversal or pullback)
• Values below -50 suggest oversold conditions (potential reversal or bounce)
Trading Strategies
Trend Following:
• Enter long positions when the signal line turns teal and shows an uptrend
• Enter short positions when the signal line turns magenta and shows a downtrend
• Use the slow signal line (area fill) as confirmation of the underlying trend
Counter-Trend Trading:
• Look for divergences between price and the indicator
• Consider profit-taking when the indicator reaches overbought/oversold areas
• Wait for trend shift signals before entering counter-trend positions
Multiple Timeframe Analysis:
• Use the indicator across different timeframes for confirmation
• Higher timeframe signals carry more weight than lower timeframe signals
Best Practices
• Experiment with different kernel types for various market conditions
• Gaussian kernels often work well in ranging markets
• Exponential kernels can provide earlier signals in trending markets
• Combine with volume analysis for higher probability trades
• Use appropriate stop-loss levels as the indicator does not guarantee price movements
This indicator is provided as-is with no guarantees of profit. Always use proper risk management when trading with any technical indicator. Nothing is financial advise.
Phát hành các Ghi chú
Updates to Coloring UIMã nguồn mở
Theo đúng tinh thần TradingView, tác giả của tập lệnh này đã công bố nó dưới dạng mã nguồn mở, để các nhà giao dịch có thể xem xét và xác minh chức năng. Chúc mừng tác giả! Mặc dù bạn có thể sử dụng miễn phí, hãy nhớ rằng việc công bố lại mã phải tuân theo Nội quy.
Free Analysis Platform 👉 alphanatt.com
Thông báo miễn trừ trách nhiệm
Thông tin và các ấn phẩm này không nhằm mục đích, và không cấu thành, lời khuyên hoặc khuyến nghị về tài chính, đầu tư, giao dịch hay các loại khác do TradingView cung cấp hoặc xác nhận. Đọc thêm tại Điều khoản Sử dụng.
Mã nguồn mở
Theo đúng tinh thần TradingView, tác giả của tập lệnh này đã công bố nó dưới dạng mã nguồn mở, để các nhà giao dịch có thể xem xét và xác minh chức năng. Chúc mừng tác giả! Mặc dù bạn có thể sử dụng miễn phí, hãy nhớ rằng việc công bố lại mã phải tuân theo Nội quy.
Free Analysis Platform 👉 alphanatt.com
Thông báo miễn trừ trách nhiệm
Thông tin và các ấn phẩm này không nhằm mục đích, và không cấu thành, lời khuyên hoặc khuyến nghị về tài chính, đầu tư, giao dịch hay các loại khác do TradingView cung cấp hoặc xác nhận. Đọc thêm tại Điều khoản Sử dụng.