OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Buy When There's Blood in the Streets Strategy
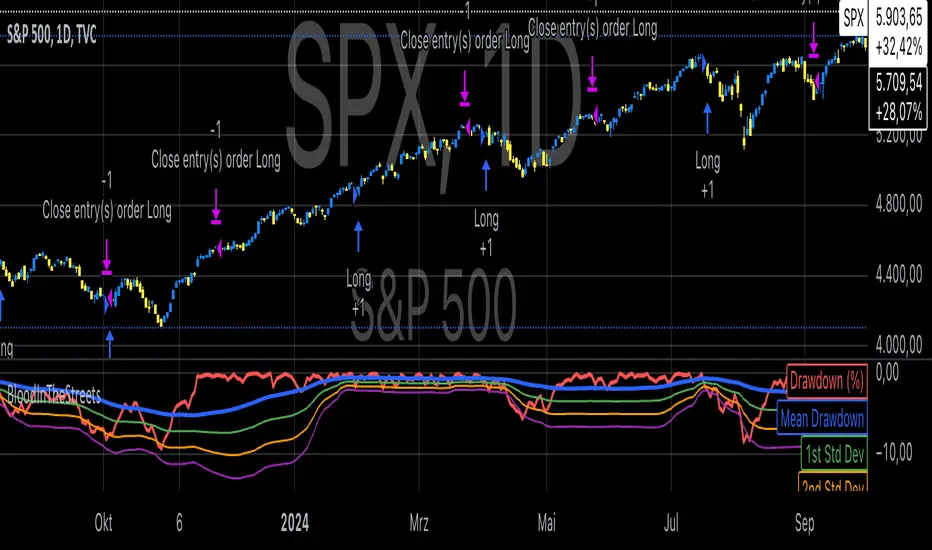
Statistical Analysis of Drawdowns in Stock Markets
Drawdowns, defined as the decline from a peak to a trough in asset prices, are an essential measure of risk and market dynamics. Their statistical properties provide insights into market behavior during extreme stress periods.
Distribution of Drawdowns: Research suggests that drawdowns follow a power-law distribution, implying that large drawdowns, while rare, are more frequent than expected under normal distributions (Sornette et al., 2003).
Impacts of Extreme Drawdowns: During significant drawdowns (e.g., financial crises), the average recovery time is significantly longer, highlighting market inefficiencies and behavioral biases. For example, the 2008 financial crisis led to a 57% drawdown in the S&P 500, requiring years to recover (Cont, 2001).
Using Standard Deviations: Drawdowns exceeding two or three standard deviations from their historical mean are often indicative of market overreaction or capitulation, creating contrarian investment opportunities (Taleb, 2007).
Behavioral Finance Perspective: Investors often exhibit panic-selling during drawdowns, leading to oversold conditions that can be exploited using statistical thresholds like standard deviations (Kahneman, 2011).
Practical Implications: Studies on mean reversion show that extreme drawdowns are frequently followed by periods of recovery, especially in equity markets. This underpins strategies that "buy the dip" under specific, statistically derived conditions (Jegadeesh & Titman, 1993).
References:
Sornette, D., & Johansen, A. (2003). Stock market crashes and endogenous dynamics.
Cont, R. (2001). Empirical properties of asset returns: stylized facts and statistical issues. Quantitative Finance.
Taleb, N. N. (2007). The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable.
Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, Fast and Slow.
Jegadeesh, N., & Titman, S. (1993). Returns to Buying Winners and Selling Losers: Implications for Stock Market Efficiency.
Drawdowns, defined as the decline from a peak to a trough in asset prices, are an essential measure of risk and market dynamics. Their statistical properties provide insights into market behavior during extreme stress periods.
Distribution of Drawdowns: Research suggests that drawdowns follow a power-law distribution, implying that large drawdowns, while rare, are more frequent than expected under normal distributions (Sornette et al., 2003).
Impacts of Extreme Drawdowns: During significant drawdowns (e.g., financial crises), the average recovery time is significantly longer, highlighting market inefficiencies and behavioral biases. For example, the 2008 financial crisis led to a 57% drawdown in the S&P 500, requiring years to recover (Cont, 2001).
Using Standard Deviations: Drawdowns exceeding two or three standard deviations from their historical mean are often indicative of market overreaction or capitulation, creating contrarian investment opportunities (Taleb, 2007).
Behavioral Finance Perspective: Investors often exhibit panic-selling during drawdowns, leading to oversold conditions that can be exploited using statistical thresholds like standard deviations (Kahneman, 2011).
Practical Implications: Studies on mean reversion show that extreme drawdowns are frequently followed by periods of recovery, especially in equity markets. This underpins strategies that "buy the dip" under specific, statistically derived conditions (Jegadeesh & Titman, 1993).
References:
Sornette, D., & Johansen, A. (2003). Stock market crashes and endogenous dynamics.
Cont, R. (2001). Empirical properties of asset returns: stylized facts and statistical issues. Quantitative Finance.
Taleb, N. N. (2007). The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable.
Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, Fast and Slow.
Jegadeesh, N., & Titman, S. (1993). Returns to Buying Winners and Selling Losers: Implications for Stock Market Efficiency.
Mã nguồn mở
Theo đúng tinh thần TradingView, tác giả của tập lệnh này đã công bố nó dưới dạng mã nguồn mở, để các nhà giao dịch có thể xem xét và xác minh chức năng. Chúc mừng tác giả! Mặc dù bạn có thể sử dụng miễn phí, hãy nhớ rằng việc công bố lại mã phải tuân theo Nội quy.
Where others speculate, we systematize.
edgetools.org
edgetools.org
Thông báo miễn trừ trách nhiệm
Thông tin và các ấn phẩm này không nhằm mục đích, và không cấu thành, lời khuyên hoặc khuyến nghị về tài chính, đầu tư, giao dịch hay các loại khác do TradingView cung cấp hoặc xác nhận. Đọc thêm tại Điều khoản Sử dụng.
Mã nguồn mở
Theo đúng tinh thần TradingView, tác giả của tập lệnh này đã công bố nó dưới dạng mã nguồn mở, để các nhà giao dịch có thể xem xét và xác minh chức năng. Chúc mừng tác giả! Mặc dù bạn có thể sử dụng miễn phí, hãy nhớ rằng việc công bố lại mã phải tuân theo Nội quy.
Where others speculate, we systematize.
edgetools.org
edgetools.org
Thông báo miễn trừ trách nhiệm
Thông tin và các ấn phẩm này không nhằm mục đích, và không cấu thành, lời khuyên hoặc khuyến nghị về tài chính, đầu tư, giao dịch hay các loại khác do TradingView cung cấp hoặc xác nhận. Đọc thêm tại Điều khoản Sử dụng.