OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Decaying Rate of Change Non Linear Filter
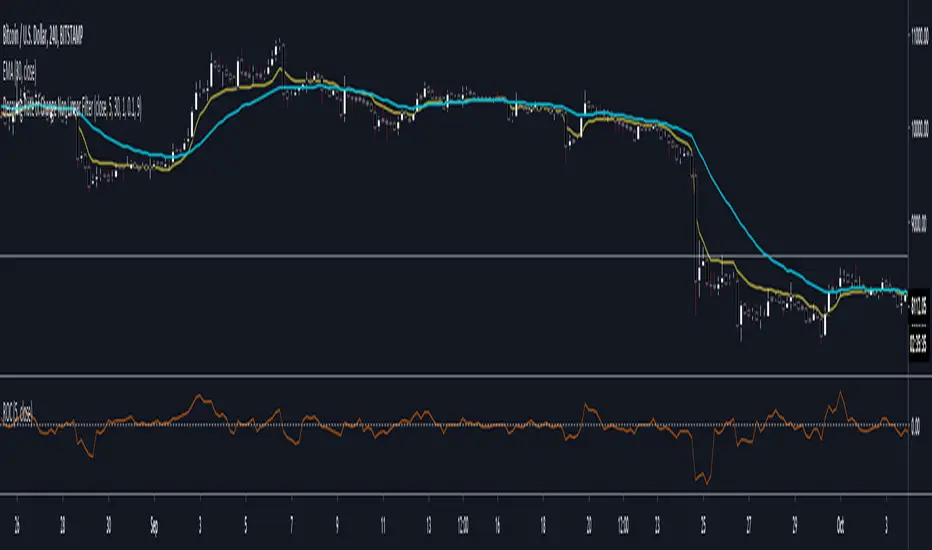
This is a potential solution to dealing with the inherent lag in most filters especially with instruments such as BTC and the effects of long periods of low volatility followed by massive volatility spikes as well as whipsaws/barts etc.
We can try and solve these issues in a number of ways, adaptive lengths, dynamic weighting etc. This filter uses a non linear weighting combined with an exponential decay rate.
With the non linear weighting the filter can become very responsive to sudden volatility spikes. We can use a short length absolute rate of change as a method to improve weighting of relative high volatility.
c1 = abs(close - close[n]) / close[n]
Which gives us a fairly simple filter :
filter = sum(c1 * close,periods) / sum(c1,periods)
At this point if we want to control the relative magnitude of the ROC coefficients we can do so by raising it to a power.
c2 = pow(c1, x)
Where x approaches zero the coefficient approaches 1 or a linear filter. At x = 1 we have an unmodified coefficient and higher values increase the relative magnitude of the response. As an extreme example with x = 10 we effectively isolate the highest ROC candle within the window (which has some novel support resistance horizontals as those closes are often important). This controls the degree of responsiveness, so we can magnify the responsiveness, but with the trade off of overshoot/persistence.

So now we have the problem whereby that a highly weighted data point from a high volatility event persists within the filter window. And to a possibly extreme degree, if a reversal occurs we get a potentially large "overshoot" and in a way actually induced a large amount of lag for future price action.
This filter compensates for this effect by exponentially decaying the abs(ROC) coefficient over time, so as a high volatility event passes through the filter window it receives exponentially less weighting allowing more recent prices to receive a higher relative weighting than they would have.
c3 = c2 * pow(1 - percent_decay, periods_back)
This is somewhat similar to an EMA, however with an EMA being recursive that event will persist forever (to some degree) in the calculation. Here we are using a fixed window, so once the event is behind the window it's completely removed from the calculation
I've added Ehler's Super Smoother as an optional smoothing function as some highly non linear settings benefit from smoothing. I can't remember where I got the original SS code snippet, so if you recognize it as yours msg me and I'll link you here.
We can try and solve these issues in a number of ways, adaptive lengths, dynamic weighting etc. This filter uses a non linear weighting combined with an exponential decay rate.
With the non linear weighting the filter can become very responsive to sudden volatility spikes. We can use a short length absolute rate of change as a method to improve weighting of relative high volatility.
c1 = abs(close - close[n]) / close[n]
Which gives us a fairly simple filter :
filter = sum(c1 * close,periods) / sum(c1,periods)
At this point if we want to control the relative magnitude of the ROC coefficients we can do so by raising it to a power.
c2 = pow(c1, x)
Where x approaches zero the coefficient approaches 1 or a linear filter. At x = 1 we have an unmodified coefficient and higher values increase the relative magnitude of the response. As an extreme example with x = 10 we effectively isolate the highest ROC candle within the window (which has some novel support resistance horizontals as those closes are often important). This controls the degree of responsiveness, so we can magnify the responsiveness, but with the trade off of overshoot/persistence.
So now we have the problem whereby that a highly weighted data point from a high volatility event persists within the filter window. And to a possibly extreme degree, if a reversal occurs we get a potentially large "overshoot" and in a way actually induced a large amount of lag for future price action.
This filter compensates for this effect by exponentially decaying the abs(ROC) coefficient over time, so as a high volatility event passes through the filter window it receives exponentially less weighting allowing more recent prices to receive a higher relative weighting than they would have.
c3 = c2 * pow(1 - percent_decay, periods_back)
This is somewhat similar to an EMA, however with an EMA being recursive that event will persist forever (to some degree) in the calculation. Here we are using a fixed window, so once the event is behind the window it's completely removed from the calculation
I've added Ehler's Super Smoother as an optional smoothing function as some highly non linear settings benefit from smoothing. I can't remember where I got the original SS code snippet, so if you recognize it as yours msg me and I'll link you here.
Mã nguồn mở
Theo đúng tinh thần TradingView, tác giả của tập lệnh này đã công bố nó dưới dạng mã nguồn mở, để các nhà giao dịch có thể xem xét và xác minh chức năng. Chúc mừng tác giả! Mặc dù bạn có thể sử dụng miễn phí, hãy nhớ rằng việc công bố lại mã phải tuân theo Nội quy.
Thông báo miễn trừ trách nhiệm
Thông tin và các ấn phẩm này không nhằm mục đích, và không cấu thành, lời khuyên hoặc khuyến nghị về tài chính, đầu tư, giao dịch hay các loại khác do TradingView cung cấp hoặc xác nhận. Đọc thêm tại Điều khoản Sử dụng.
Mã nguồn mở
Theo đúng tinh thần TradingView, tác giả của tập lệnh này đã công bố nó dưới dạng mã nguồn mở, để các nhà giao dịch có thể xem xét và xác minh chức năng. Chúc mừng tác giả! Mặc dù bạn có thể sử dụng miễn phí, hãy nhớ rằng việc công bố lại mã phải tuân theo Nội quy.
Thông báo miễn trừ trách nhiệm
Thông tin và các ấn phẩm này không nhằm mục đích, và không cấu thành, lời khuyên hoặc khuyến nghị về tài chính, đầu tư, giao dịch hay các loại khác do TradingView cung cấp hoặc xác nhận. Đọc thêm tại Điều khoản Sử dụng.